B-SHADE Estimation and
Sampling Manual
B-SHADE Theory
Sampling
is a method to investigate and understand the population using a sample. It has
been widely applied in various disciplines such as natural resources,
environmental pollution, and public health. With the sample data collected,
some parameters of the population (for example, mean and sum) is estimated
using an appropriate model. Usually, a best and unbiased estimation is
expected. However, if the samples were not carefully selected under the model's
assumption, then the estimated result is biased from the population's real
value. For example, when setting sentinels to estimate a disease's prevalence
or incidence in a city, hospitals with good equipment and doctors are more
likely to be selected by planners. Then the sentinels' average visitor number
would be much higher than the real average visitor number of all hospitals. By
considering the correlation between samples and their population, the B-SHADE
(Biased Sentinel Hospital based Area Disease Estimation) model can generate an
unbiased estimation of the population with biased samples. Although originally
designed for biased sentinel hospitals' patient number/incidence estimation, it
is a common method for biased samples’ population estimation.
Software Functionality
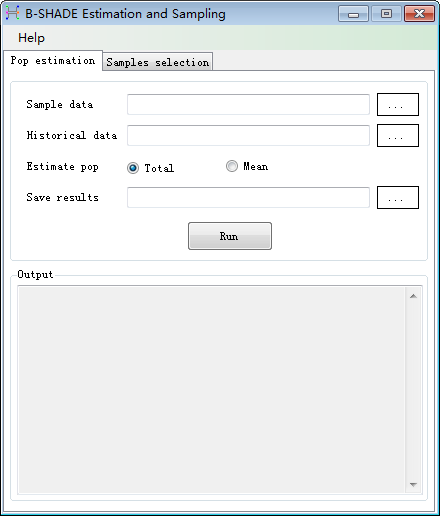
1. Pop estimation
(1) Menu bar
Wizard:
including two main functions, Pop estimation and Samples selection.
Help:
showing the manual, demo and about of the system.
(2) Data input
area
Input
the sample data and historical data, choose total or mean population to
estimate.
(3) Result
output area
Result
is shown in a table, including Date, the estimated total (or mean) population
and the variance. Export the result in CSV format.
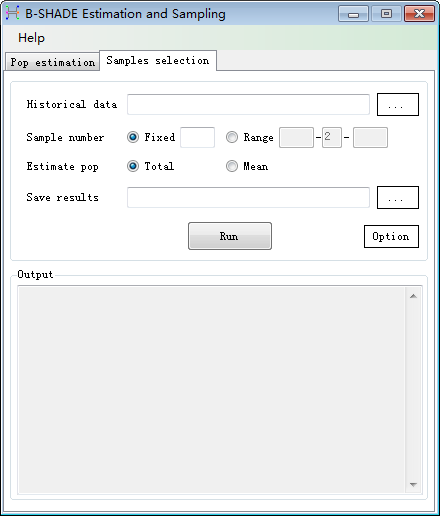
2. Samples selection
(1) Data input
area
Input
historical data and the required number of sample stations.
Advanced
options about the simulated anealing optimisation can be setted by click the
"Options" buttun.
(2) Result
output area
System
displays the best sample combination in a grid.